When Gina noticed her daughter Francesca wasn’t hitting her gross motor milestones, she turned to...
Read MoreWinter Weather Update: Some of our locations are closed or have delayed openings Monday, February 23rd. View the full list of status updates here.
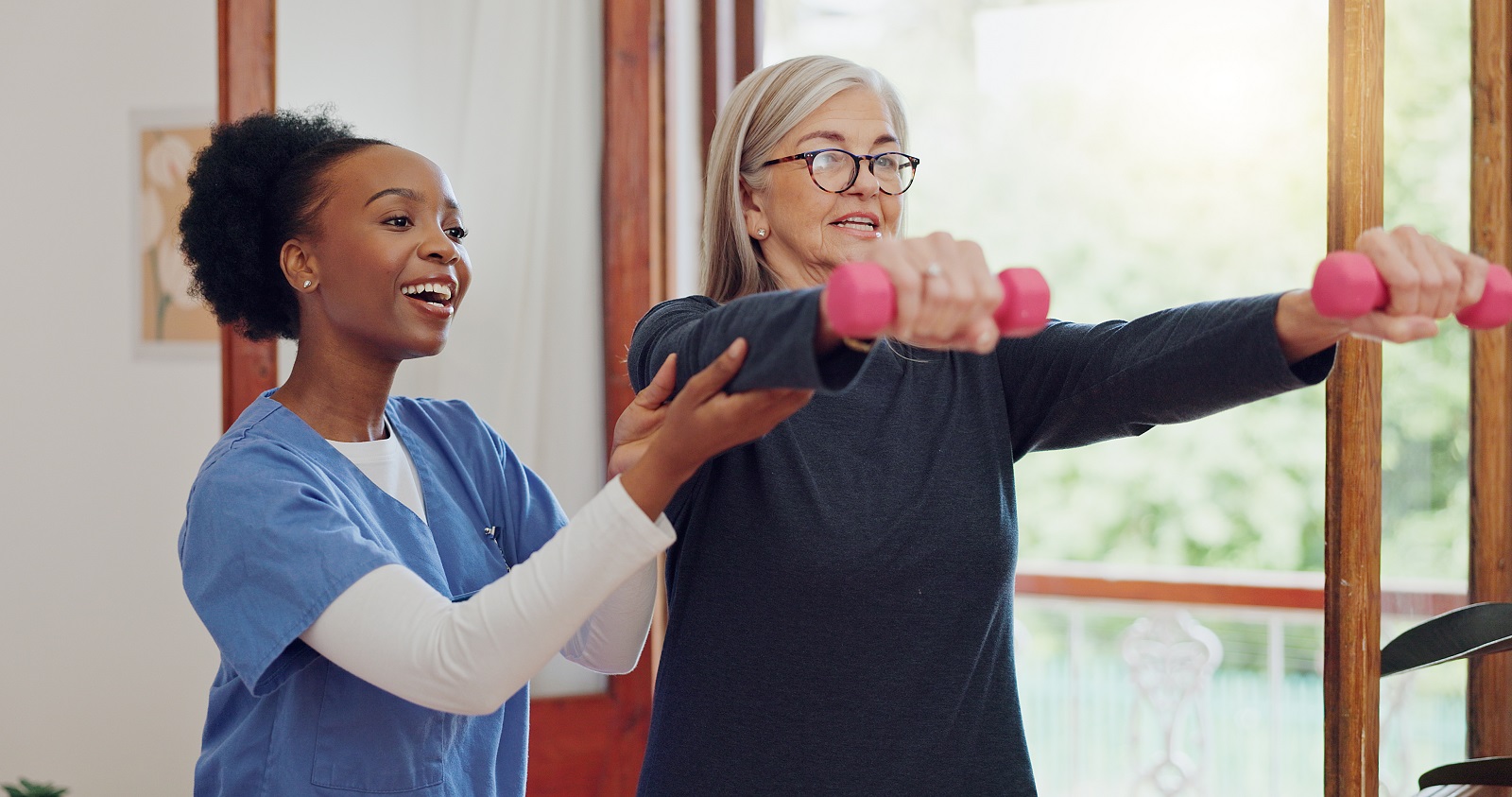

A rotator cuff tear can make everyday activities—such as reaching overhead, lifting or sleeping—painful and difficult. With the right treatment, most people regain strength, restore shoulder mobility and return to the activities they enjoy.
A rotator cuff tear is an injury to one or more of the tendons that stabilize and move your shoulder. These tendons connect muscles to the bones of the shoulder joint, allowing you to lift, rotate and reach overhead. When a tendon becomes partially or fully torn, pain and weakness can limit your ability to use the arm comfortably.
Rotator cuff tears are described in different ways depending on how much of the tendon is damaged and how the injury occurred:
Rotator cuff tears may result from sudden trauma, such as falling on an outstretched arm, or from gradual wear and tear over time. Repetitive overhead movements in sports, heavy lifting or age-related degeneration are common causes. Risk increases with age, smoking and jobs or activities that place repeated stress on the shoulder.
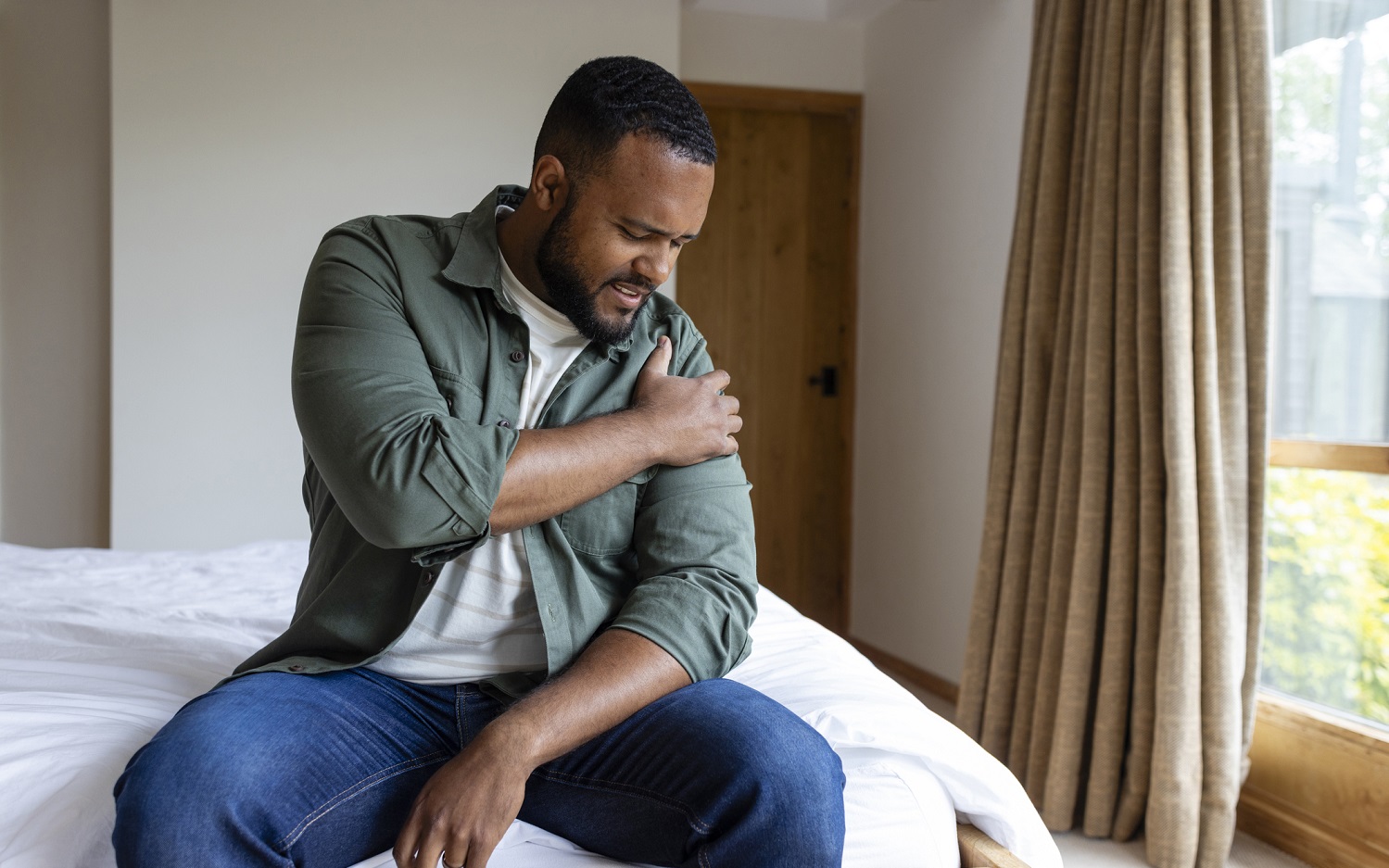
Symptoms of a rotator cuff tear can range from mild discomfort to significant loss of shoulder function. They may develop suddenly after an injury or gradually over time due to ongoing wear and tear. Symptoms may include:
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, how the injury occurred and examine your shoulder for muscle anatomy, strength, and range of motion. Imaging tests like X-rays and MRI or ultrasound help confirm the diagnosis and reveal partial or complete tears. Treatment options will be discussed based on your needs and goals.
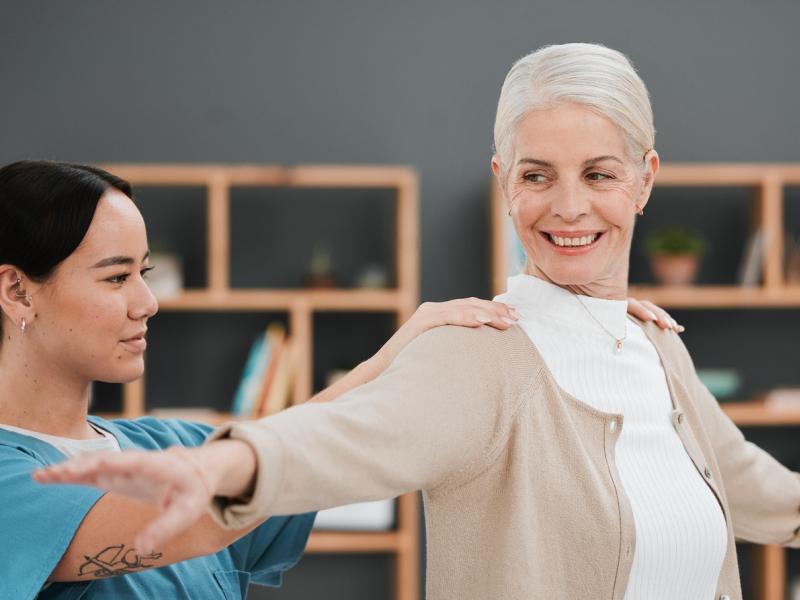


Exercises for a torn rotator cuff help strengthen surrounding muscles, improve range of motion and support shoulder stability. Therapy is often the first step in the treatment process.
When tears are large, complete or unresponsive to conservative care, surgery may be needed to reattach the tendon to the bone.
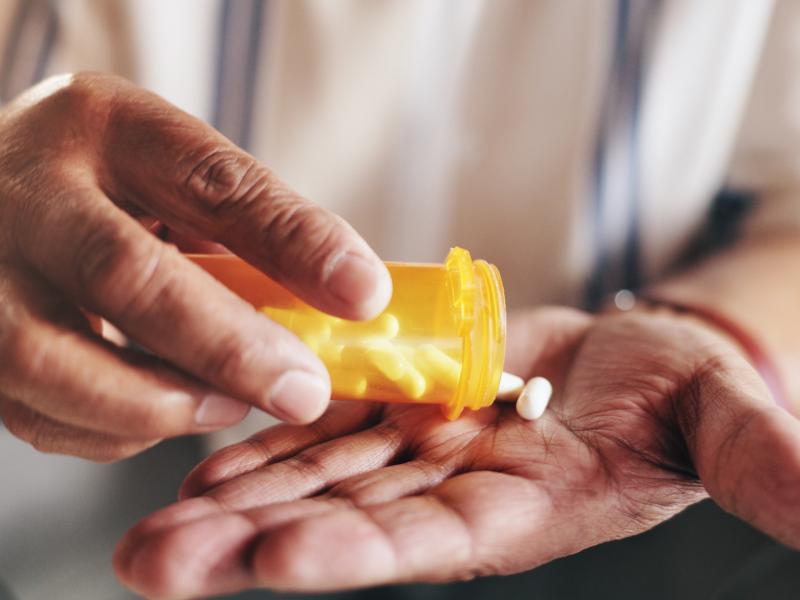

Cold packs, warm compresses and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can ease pain and swelling in the shoulder.
For persistent pain, injections directly into the shoulder joint may provide temporary relief and reduce inflammation.
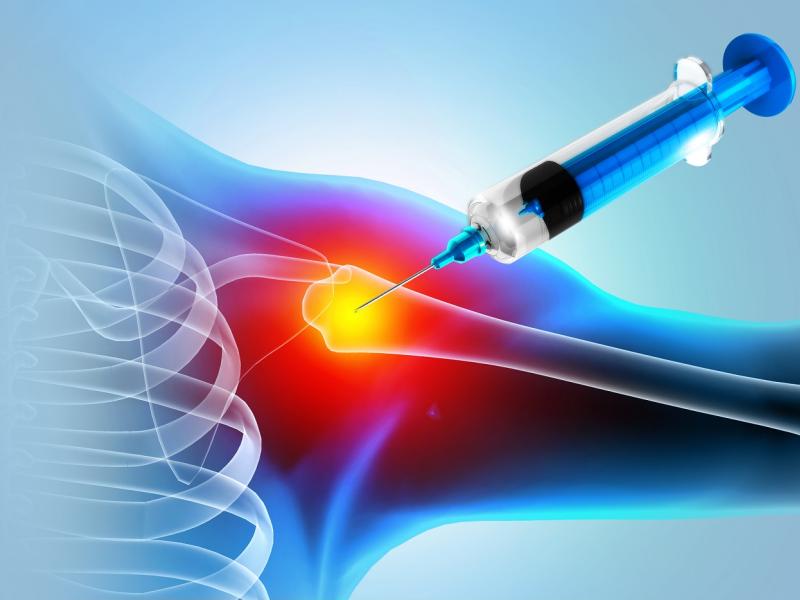
In some cases, PRP injections are used to stimulate tendon healing, though results may vary.

Rehabilitation after surgery is crucial for restoring strength and mobility. Recovery typically includes several months of structured Physical or Occupational Therapy.
Avoiding overhead or heavy lifting movements can help reduce strain on the shoulder and allow inflammation to subside.
Rotator cuff care at Inspira begins with a thorough evaluation to understand the extent of the injury and its impact on your daily activities. Our specialists create a personalized plan that may include activity modification, Physical/Occupational Therapy and advanced treatments to reduce pain and restore shoulder strength.
When surgery is required, our orthopedic surgeons and rehabilitation team work together to provide seamless, coordinated care. Post-surgical therapy focuses on rebuilding mobility, strengthening surrounding muscles and preventing reinjury. With access to certified rehabilitation clinicians and advanced therapies, we help patients regain function and return to work, hobbies or athletics with confidence.
A rotator cuff tear often feels like pain or weakness when lifting or rotating the arm. Many people notice difficulty performing overhead activities or reaching behind the back. Some describe a dull ache that worsens with use or at night, especially when lying on the affected shoulder.
Two common warning signs are persistent shoulder pain that does not improve with rest and weakness or difficulty lifting the arm above shoulder height. If these symptoms last more than a few weeks, it may indicate a tear and should be evaluated by a doctor.
Not always. Some tears cause constant pain, while others only hurt during activity or at night. Pain often worsens with reaching, lifting or repetitive arm use. Over time, untreated tears may become more painful and can lead to stiffness or loss of shoulder mobility.
No, not every rotator cuff tear requires surgery. Many partial tears improve with rest, Physical/Occupational Therapy and injections. Doctors usually recommend surgery for complete tears, large tears or cases where more conservative treatments have not relieved pain or restored function.
Recovery depends on the severity of the tear and the treatment used. Mild tears may improve in a few months with therapy, while recovery after surgery often takes six to 12 months. Consistent rehabilitation is key to regaining full shoulder strength and function.

When Gina noticed her daughter Francesca wasn’t hitting her gross motor milestones, she turned to...
Read More
Sports medicine and physical therapy both play vital roles in injury recovery, but they serve...
Read More
Whether you’re a weekend warrior or a seasoned competitor, a few strength and mobility tips can go a...
Read More