Paul Maurice turned to Inspira Rehab Services for pain relief and mobility after an ankle injury. He...
Read More
Stroke is a serious medical condition that happens when blood flow to part of the brain is blocked or a blood vessel bursts. It can cause lasting brain damage, but quick treatment can reduce complications and improve outcomes.
A stroke happens when blood flow to a part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, preventing brain tissue from getting the oxygen and nutrients it needs. Within minutes, brain cells begin to die. Stroke is a medical emergency, and early treatment is essential to minimize brain damage and improve the chances of recovery. Depending on which part of the brain is affected, stroke can affect movement, speech, memory and other vital functions.
There are different types of stroke, each with its own cause and treatment approach:
Common medical risks include high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol and atrial fibrillation. Carotid artery disease, where arteries in the neck are narrowed or blocked, also increases stroke risk. Lifestyle habits like smoking, excessive alcohol use, unhealthy diet and physical inactivity further elevate risk. Age, family history and certain health issues also play a part.
Stroke symptoms often come on suddenly and can vary depending on the part of the brain affected. Symptoms include:
Doctors start with physical exams, symptom review and brain imaging to identify the type and location of the stroke. A CT scan, which can quickly detect bleeding in the brain and an MRI can provide a more detailed view of brain tissue and confirm an earlier or more minor stroke. Tests such as a carotid ultrasound, echocardiogram or blood tests can help identify underlying causes, including blocked arteries, heart issues or clotting problems.
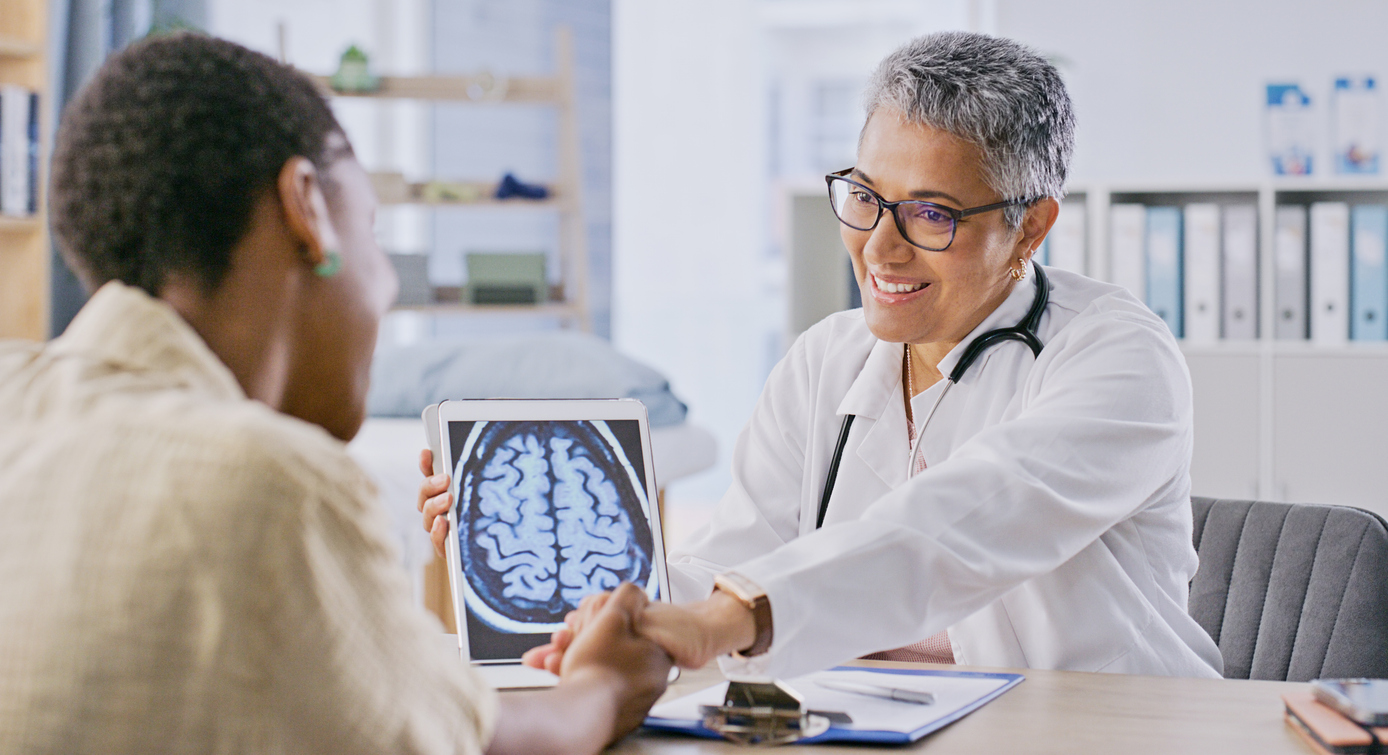

After the initial treatment, many people benefit from physical, occupational and speech therapy to regain independence and improve their quality of life.
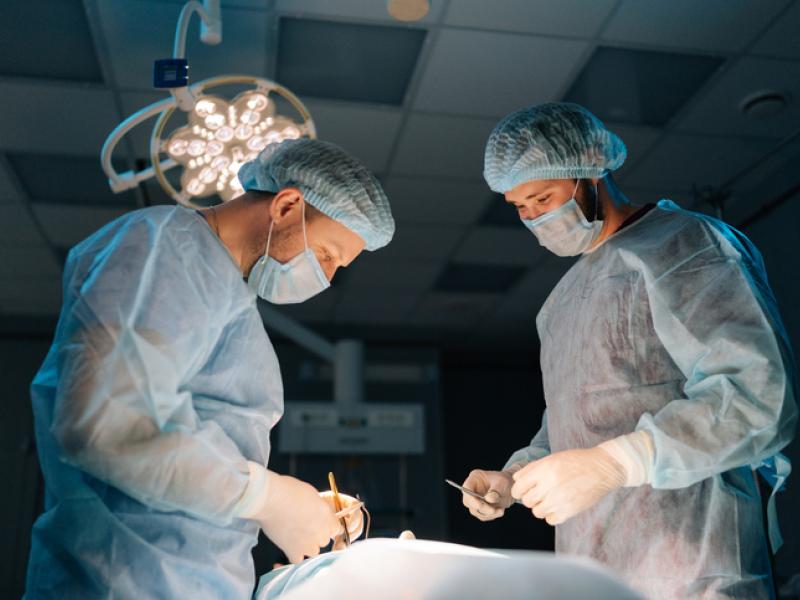
A less invasive alternative to endarterectomy, CAS uses a catheter, usually via the groin, to place a stent in the carotid artery. It restores blood flow but carries a slightly higher risk of embolic stroke compared with transcarotid artery revascularization (TCAR).

A less invasive alternative to traditional carotid surgery, TCAR safely reduces stroke risk in patients with carotid artery disease through a small incision and advanced stenting techniques. It offers a lower risk of complications and is one of the latest advancements in stroke prevention.

This surgical procedure removes plaque buildup from the carotid artery in the neck to restore proper blood flow and prevent a future stroke.

For ischemic stroke, medications or thrombolytics like tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) can dissolve blood clots if given within a few hours of symptom onset.
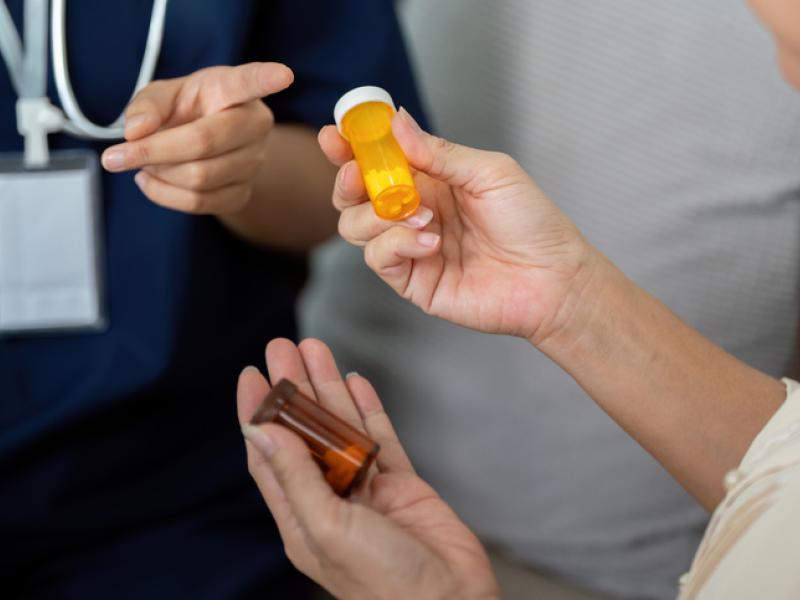
Medications such as aspirin or blood thinners help prevent new clots from forming, especially after a TIA or mild stroke.
At Inspira, we deliver fast, expert stroke care focused on rapid diagnosis, advanced treatment and ongoing recovery. Our team includes neurologists, vascular surgeons, emergency medicine providers, interventional radiologists and rehabilitation specialists who work together to provide seamless, personalized care. We use state-of-the-art options like TCAR for carotid artery disease to lower stroke risk. From emergency intervention to rehab and prevention, we support you through every stage of your stroke journey.
While many stroke symptoms are the same for all people, women and AFAB individuals may experience additional or subtler warning signs. These can include fatigue, confusion, general weakness, shortness of breath, nausea and hiccups. Recognizing early symptoms, including sudden numbness, trouble speaking or vision changes, is critical, regardless of how mild they seem.
People experiencing a stroke often describe it as a sudden and unexpected event. You may feel numbness or weakness on one side of the body, confusion, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, dizziness or trouble walking. It can also feel like the worst headache of your life, especially with a hemorrhagic stroke.
A stroke is caused by either a blockage of blood flow to the brain (ischemic stroke) or bleeding in the brain (hemorrhagic stroke). Causes may include high blood pressure, blood clots, artery disease, trauma or aneurysm rupture. Underlying conditions like atrial fibrillation or diabetes also increase the risk of stroke.
Blood pressure readings of 180/120 mm Hg or higher are considered hypertensive crisis levels and can put someone at immediate risk of stroke. If you experience this level of blood pressure along with symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath or weakness, seek emergency care immediately.
Stroke prevention focuses on managing risk factors like high blood pressure, cholesterol, diabetes and heart conditions. Avoiding smoking, exercising regularly, eating a balanced diet and limiting alcohol intake also play a vital role. Your doctor may recommend medications and procedures that can prevent stroke if you manage conditions like carotid artery disease.



Paul Maurice turned to Inspira Rehab Services for pain relief and mobility after an ankle injury. He...
Read More
Blood clots can happen to anyone, even elite athletes. Here’s what to know about how blood clots...
Read More
Varicose veins are twisted, enlarged veins that can cause discomfort, swelling and circulatory...
Read More